Time Machine
Reference - https://liaoxuefeng.com/books/git/tag/push-delete/index.html
1. Modify the file content
Original file content :
Git is a version control system.
Git is free software.
Update to :
Git is a distributed version control system.
Git is free software.
git status The command allows us to keep track of the current status of the repository. (Staged / Unstage status)
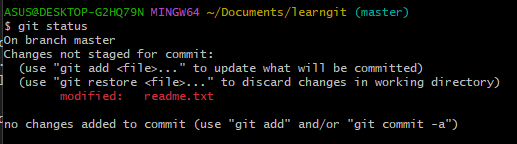
git diff <file name> you can see the changes that has been modified.
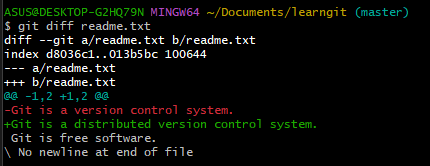
Summary
- To keep track of the status of your workspace at all times, use
git statuscommands.- If
git statusit tells you that a file has been modified,git diffcan view the modified content.
2. Version Rollback
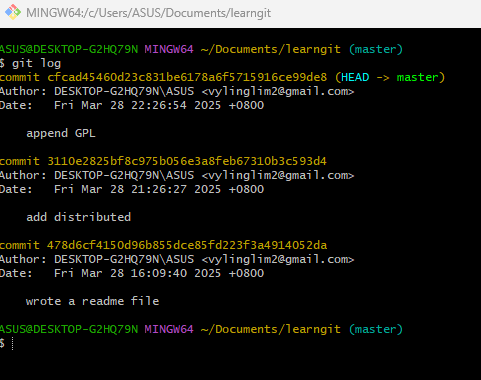
Use git log command to view commit history
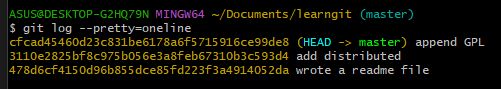
Use git log --pretty=oneline when too dazzling
The long string of similar numbers you see 1094adb...is commit id(version number)
- Make readme.md rollback to
add distributedversion
HEADis the current version is represented by , which is the latest commit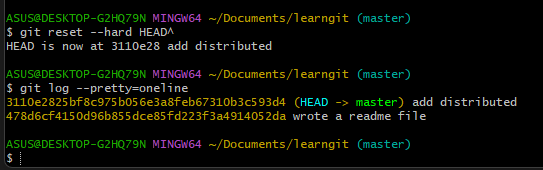
- use
git reset --hard HEAD^
--hard It will roll back to the last version's committed state
--soft will roll back to the last version's uncommitted state, and
--mixed it will roll back to the last version's added but uncommitted state.
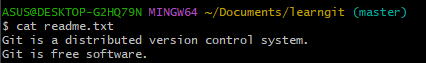
Check readme.txt if the content is the version add distributed:
- use
cat <file name>
To restore the append GPL(cfcad45460d23c831be6178a6f5715916ce99de8) that have been reset:
- As long as the command line window above has not been closed, you can search up and find the one append GPLt commit id
- use
git reset --hard <commit id>
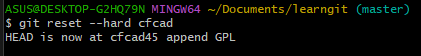
When you forgot the commit id, you can use git reflog to find.
Summary
HEADThe version pointed to is the current version, so Git allows us to shuttle between version histories using commandsgit reset --hard <commit_id>- Before reverting,
git logcan view the commit history to determine which version to revert to.- To go back to the future, use
git reflogto view the command history so that you can determine which version in the future you want to go back to.
3. Undo Modification
git checkout -- <file> This command discard all changes to the file in the workspace / unstage changes.
git reset HEAD <file> can use commands to undo (unstage) the changes in the temporary storage area and put them back into the working area.
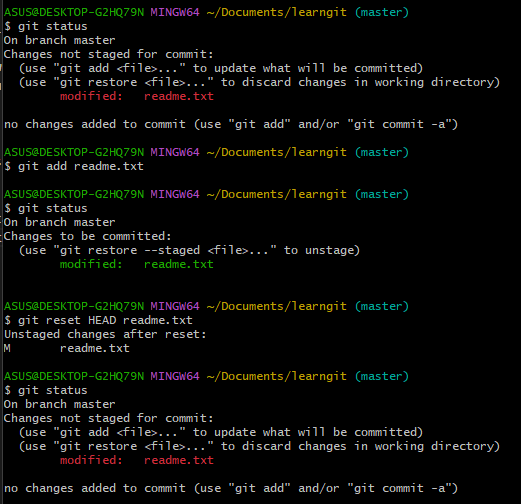
4. Delete file
rm <file> This delete file command.